Autobà – Everything That You Need To Know In 2024!
In the vast fabric of nature, autobàs are like tiny but vital threads, working silently to maintain ecological harmony. These unremarkable insects may be invisible, but their role in recycling nutrients through decomposition is crucial for the health of our environment.
This article will guide you through the details about the autobà and their proper life cycle. Now, let’s move towards it!
Characteristics Of Autobà – Its Unique Traits!
1. Physical Attributes:
Autobàs are small, typically ranging from a few millimeters to a centimeter in size. Their exoskeletons, which come in various colors, protect their segmented bodies. Like any other insect, they have six legs and a three-part body—head, thorax, and abdomen.
2. Behavior and Habits:
These nocturnal creatures prefer to go about their business under the cover of night, steering clear of larger, carnivorous insects. Their habits align with their role as decomposers, contributing to the health of their environments.
Life Cycle Of Autobà – Stages Of This Creature!
- Egg Stage: Autobàs start as tiny, well-protected eggs deposited in secret areas to increase hatching chances.
- Larva Stage: Hatched larvae have hearty appetites, mainly subsisting on dead and decaying matter, crucial for plant decomposition.
- Pupa Stage: Autobà undergoes metamorphosis from larva to adult inside a cocoon, a vital phase for their development.
- Adult Stage: Emerging from the pupa, adult autobàs resume their ecological duties, playing a key role in nutrient recycling.
- Habitat and Distribution: Autobàs are widespread, thriving in ecosystems rich in decomposing organic materials, such as city compost heaps and wooded areas.
Role Of Autobà’s As Decomposers And Their Impact On Other Species – For You!
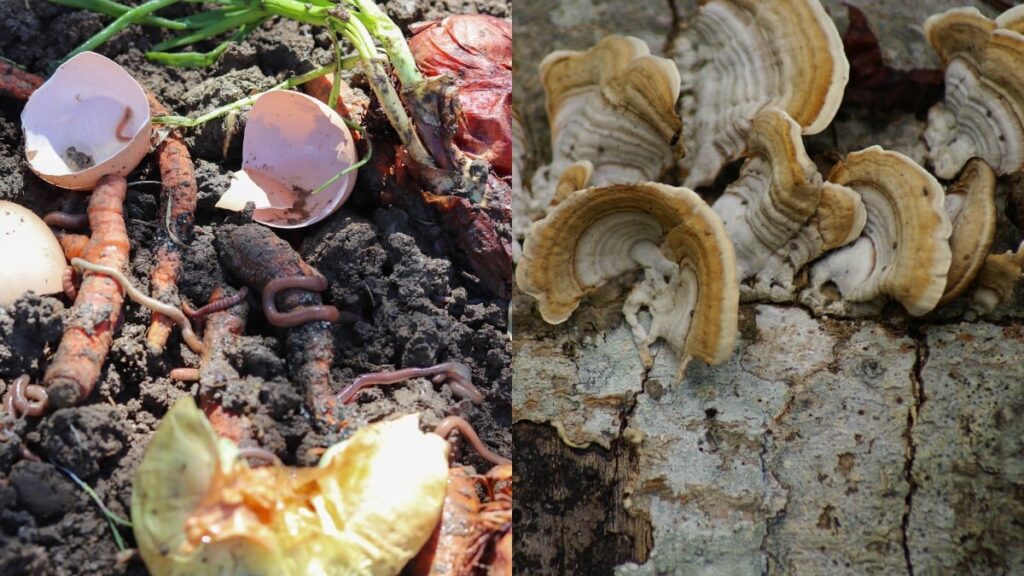

Autobàs act as nature’s recyclers, decomposing plant matter and releasing nutrients into the ground, maintaining the fragile equilibrium of ecosystems.
Their efforts enhance soil quality, supporting plant growth and providing food for herbivores and omnivores, indirectly benefiting other species.
Threats And Predators To Autobàs – Their Vulnerability!
Autobàs, despite their excellent hiding skills, face a delicate balance in the natural world. Natural predators such as birds, small animals, and other insects pose constant threats despite the insects’ excellent camouflage abilities.
However, the challenges don’t end there. Human-induced threats, including habitat destruction and the use of pesticides, cast dangerous shadows over autobà populations. These activities not only disrupt their habitats but also endanger the crucial ecological role these insects play.
This complicated situation between natural predators and human-induced threats creates a complex scenario. This highlights the need for careful conservation efforts to ensure the survival of these tiny but essential contributors to our ecosystems.
Autobà And Human Interaction – Friendship Aspect!
- Positive Aspects: Autobàs contribute to ecosystem health and agricultural soil quality, making them beneficial to humans in the long run.
- Negative Aspects: Deforestation and pesticide use are human actions that harm autobà populations and the ecosystems they support.
Autobà’s Unique Adaptations – Camouflage And Defensive Mastery!

Autobàs display an impressive range of tactics for survival, utilizing two main strategies. Firstly, their Camouflage Techniques are like skilled performances in imitation and disguise, allowing them to blend seamlessly into their surroundings and avoid the keen eyes of predators.
Secondly, their Defensive Mechanisms unveil a set of protective measures. Some autobà species, demonstrating chemical prowess, release toxic substances or emit offensive odors, serving as an effective deterrent against potential threats. This two-pronged survival strategy highlights the cleverness of autobàs in dealing with the challenges of their environment.
3 Interesting Facts About Autobà – Must Know!
- Autobà Diversity: They come in various species adapted to specific ecological niches and geographic areas.
- Role in Folklore and Culture: Autobàs have been represented in folklore and cultural legends, symbolizing various ideas in different cultures.
- The Intriguing World of Autobàs: While often portrayed as minor players in nature’s drama, autobàs play a crucial role as unsung heroes. Their tireless work in decomposition keeps the wheel of life turning, showcasing these tiny insects’ fascinating and vital role in our environment.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Why should we protect autobàs?
Protecting autobàs is crucial because these tiny insects play a vital role in maintaining the health of our ecosystems. Autobàs act as nature’s recyclers, decomposing plant matter and releasing nutrients into the ground.
2. Are Autobàs restricted to the woods?
No, Autobàs are not restricted to the woods. Autobàs are versatile insects that can thrive in diverse environments beyond wooded areas. They are found in meadows, urban compost heaps, and various ecosystems where decomposing organic materials are present.
3. Is Autobàs the subject of any conservation initiatives?
Yes, numerous groups and researchers are actively working to understand and protect Autobà populations and their natural habitats. Their efforts aim to gather more knowledge about these insects and ensure the preservation of their environments.
4. How do Autobàs avoid being eaten by predators?
Autobàs employ different ways to hide; in specific situations, they produce unpleasant smells or chemicals to avoid possible predators.
Conclude It
Autobàs are not receiving much attention, but autobàs are essential for the well-being of our ecosystems. These tiny insects, often overlooked, serve as the unsung heroes of the natural world.
Their significance lies in their pivotal role in recycling nutrients and promoting plant development. Autobàs contribute to maintaining a healthy balance in nature by decomposing organic matter, enriching the soil, and fostering the growth of various plant species.
READ MORE:
